NVIDIA GeForce RTX 50 series graphics cards – when pure performance is no longer enough
12.07.25
This year, NVIDIA introduced the Blackwell architecture, which became the basis for GeForce RTX 50-series video cards. It made it possible to make a number of algorithms and technologies even more efficient. DLSS and Frame Generation reached a new level, generating frames even better. This is achieved not only due to computing power, but also optimization for updated software algorithms and artificial intelligence elements.
About Blackwell architecture
The NVIDIA Blackwell graphics architecture is built on a modular principle. It includes two computing chiplets with a total of 104 billion transistors. It also includes eight HBM3E memory chiplets. The components are connected using CoWoS-L packaging technology developed by TSMC. The connection uses a new proprietary NV-HBI (NVIDIA High Bandwidth Interface) interface, providing a throughput of up to 10 TB/s. This allows data to be transferred between computing chiplets, minimizing delays when working with large data sets.
GDDR7 — the new video memory standard
The new GeForce RTX 50 video cards based on Blackwell received GDDR7 memory. It has a higher bit depth and throughput compared to GDDR6. In particular, in the flagship RTX 5090, GDDR7 video memory operates at a speed of 28 Gbps, which gives a throughput of up to 1.8 TB/s.
By the way, the youngest RTX 5050 in the desktop version still received GDDR6 memory like previous generations. While the laptop version has GDDR7 chips. The company argued that the new memory is more energy efficient, and therefore more relevant for portable than desktop computers. True, the frequencies of the new model are higher, so the throughput remains better in comparison. Thus, we see a fairly thin parity between business efficiency and technological update.
Fifth-generation tensor cores
The new generation of architecture implements updated tensor cores with support for FP4 and FP6 formats. Processing 4-bit numbers provides better efficiency and higher throughput. SI models can do more operations on scene analysis, motion, lighting and shadows. All this is applicable when generating additional frames in real time. And here, perhaps, it is worth moving on to the second part about the architecture update – DLSS 4 and Multi Frame Generation (MFG).
DLSS 4 – all the features
Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS) is a set of neural rendering technologies that uses artificial intelligence to increase frame rates, reduce latency, and improve image quality. This reduces the load on the GPU while maintaining the detail and clarity characteristic of native high resolution. In general, this is a complex of algorithms and AI models that have evolved over the past years. DLSS 4 is the current version supported on RTX series video cards, including the new 50xx series models. Previous generations of video cards also support some image enhancement technologies, including Super Resolution, DLAA, and Ray Reconstruction. You can enable the function in games that support frame generation.

The fourth generation of NVIDIA’s Deep Learning Super Sampling (DLSS 4) scaling technology has received a number of significant changes. In this generation, the main components are two main components – a new transformation model instead of the traditional CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) model and MFG (Multi-Frame Generation), which increases FPS.
DLSS 4, together with the MFG module, which we will talk about in more detail below, shows a particularly large FPS increase in high-resolution modes. The effect increases many times with increasing resolution, since there is more visual data to process. For example, in 4K modes, where the rendering load is the largest, you can see an increase in the number of frames per second up to 8 times. Outputting many additional frames requires monitoring their switching and timings. For this, a separate High Speed HW Flip Metering module works, “monitoring” the low latency of image output.
Although we get a smoother image during the game with frame generation enabled, this does not always have a positive effect on the control sensations. The generated frames look realistic, but do not affect the system’s response to the player’s actions. Control latency remains at the same level or even increases due to additional processing.
This is why NVIDIA recommends using Multi Frame Generation frame generation, the base frame rate exceeds 60 FPS. In this case, the negative impact of latency is minimized due to the short frame time.
Multi-Frame Generation as a basis
An integral part of DLSS 4 technology is the Multi-Frame Generation system. It analyzes previous frames and generates intermediate ones. The technology began to develop in DLSS 3 Frame Generation, which generated one intermediate frame. Now we are talking about the ability to generate from 1 to 3 intermediate frames.
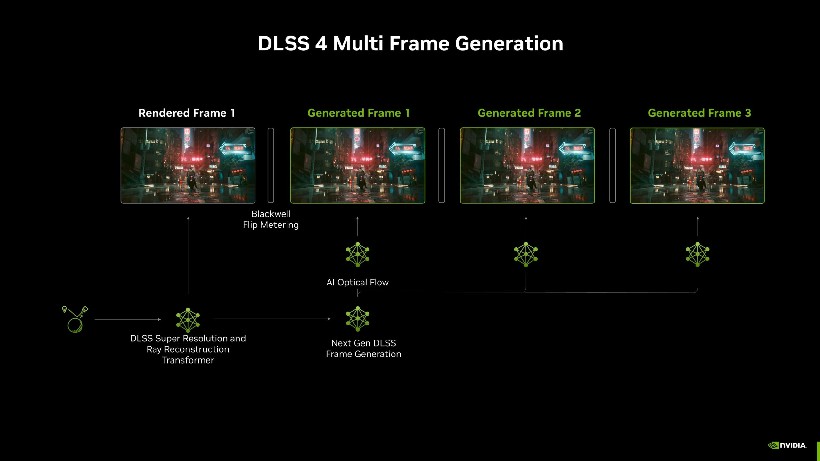
To do this, a new Transformer algorithm is used, which works better with long patterns. The technology requires twice as many parameters and four times more computing resources. At the same time, this allows the model to create a sequence of frames in real time. Instead of one intermediate frame, as in previous versions, DLSS 4 generates three at once, while maintaining low latency.
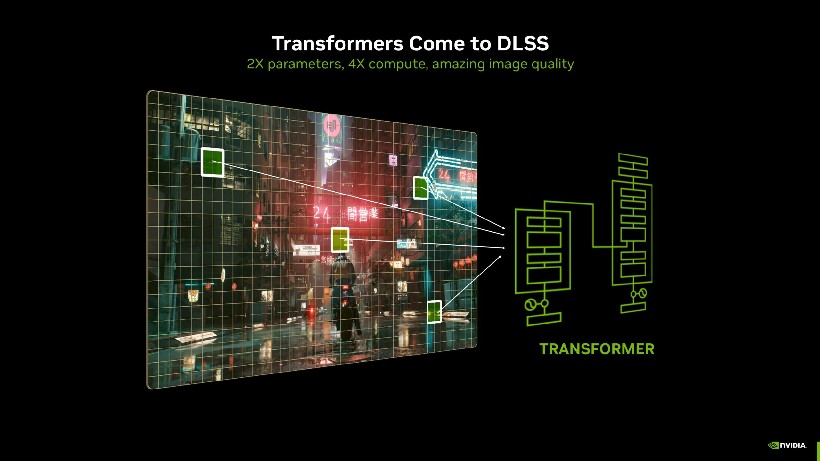
In the new version, the optical flow generation unit has been supplemented with a neural network that analyzes the current frame in the context of the previous ones, determining the significance of each pixel in the scene. Thanks to this, the system can purposefully distribute computing resources only to important areas of the image, reducing the load and increasing the efficiency of scaling. In order for the generated frames to be evenly inserted between two rendered ones, Flip Metering technology is used. It ensures a stable frame rhythm and promotes smoothness of the image without jumps or shifts in playback time.
This made it possible to increase the frame rate even in resource-intensive scenes, while maintaining visual smoothness. However, in conditions of rapid scene changes, data from two adjacent frames is sometimes insufficient for accurate generation of an intermediate one. In such situations, visual artifacts may appear – distortion, blurring or errors in details. Reflex technology partially solves this problem. It eliminates the so-called rendering queue. Typically, the CPU prepares frames faster than the graphics card (GPU) can process them, resulting in a buffer of frames waiting to be rendered. The longer this queue, the higher the delay from the moment of action to its display on the screen. Reflex synchronizes the work of the CPU and GPU, preventing the processor from unnecessarily outpacing the graphics processor, thereby reducing the overall latency in the system. When you enable frame generation in the settings, Reflex is also automatically enabled.
In addition to eliminating the rendering queue, Reflex 2 technology introduces a new approach to reducing latency – the Frame Warp mechanism. This is a frame warp that is performed immediately before the image is displayed on the screen.
Instead of displaying a frame formed from outdated input data, the system allows the processor to take into account the last mouse movement and the current camera position literally an instant before sending the frame to the display. The finished image goes through a “distortion” phase — the pixels are shifted in accordance with the latest information, providing the player with a more accurate representation of the actions performed.
Availability of DLSS technologies
Processing and organizing a large number of frames, most of which are generated by neural networks, requires additional resources and hardware, which are not available in previous generations of video cards. Most of the DLSS 4 capabilities are available on all NVIDIA RTX series video cards. At the same time, support for the key Multi-Frame Generation function is limited to RTX 50 series models only, since it requires specialized hardware units available only in this generation. An updated version of Frame Generation, which consumes less video memory thanks to a new algorithm, is also supported by RTX 4000 series video cards.

All the features we’ve described make the GeForce RTX 50 series graphics cards really interesting, and if you’re considering upgrading your PC, they’re worth considering, as Telemart already has plenty of models available.
Editor
Don't miss interesting news
Subscribe to our channels and read announcements of high-tech news, tes
Oppo A6 Pro smartphone review: ambitious

Creating new mid-range smartphones is no easy task. Manufacturers have to balance performance, camera capabilities, displays, and the overall cost impact of each component. How the new Oppo A6 Pro balances these factors is discussed in our review.
Acer Nitro Lite 16 (NL16-71G) laptop review: versatile and attractive

The 2025 Acer Nitro Lite 16 features an interesting case design, gaming accents, and proven components. Let’s take a closer look at its features.
Gartner: Entry-level PC segment will disappear by 2028 computer financials hardware statistics
Shortage of DRAM memory is beginning to affect not only the prices of individual components, but also the structure of the entire personal computer market.
MWC 2026: Lenovo ThinkBook Modular AI PC Concept unveiled – detachable display, Bluetooth keyboard, USB-A, USB-C and HDMI ports Bluetooth laptop Lenovo MWC
Lenovo introduces new ThinkBook Modular AI PC Concept, combining a detachable second display and interchangeable ports